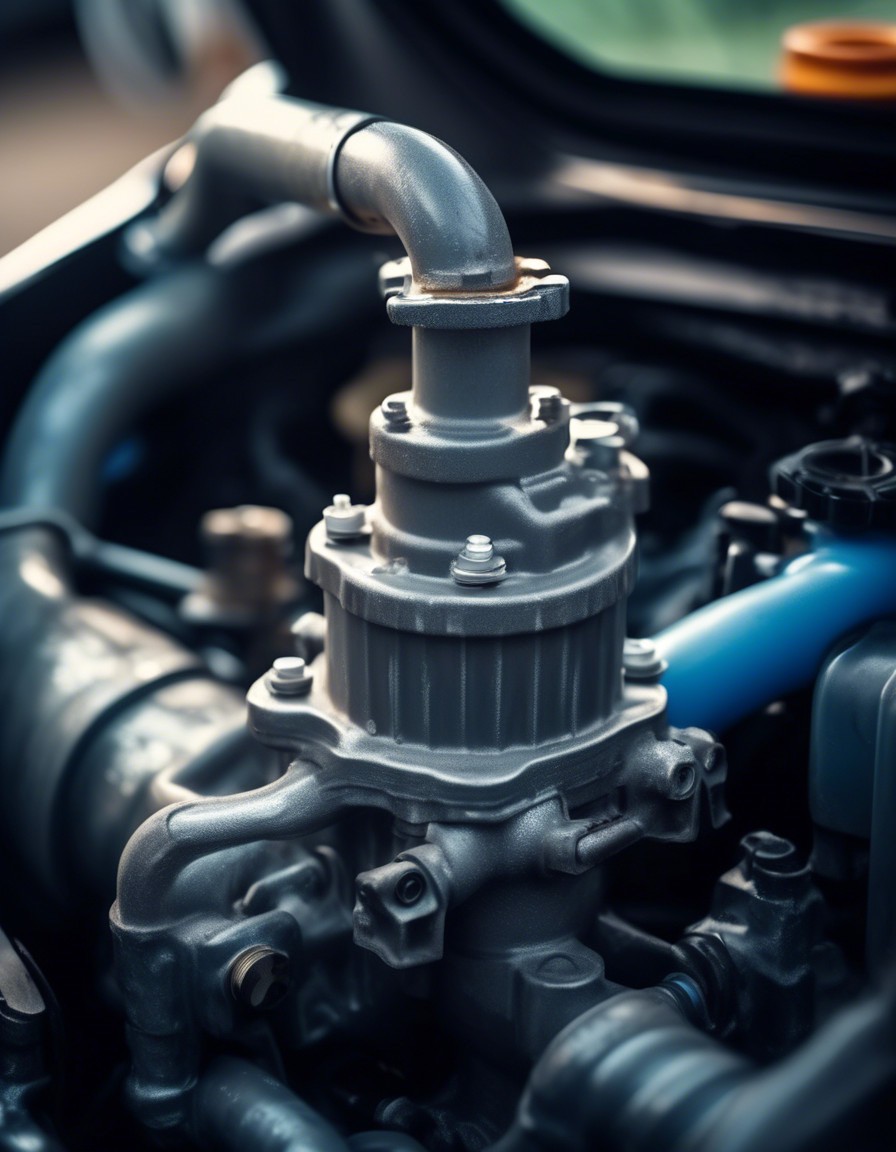
1. 워터 펌프 개요
1.1. 정의와 목적
워터 펌프는 자동차 냉각 시스템의 중요한 구성 요소로, 냉각수(물과 부동액의 혼합물)를 엔진과 라디에이터를 통해 순환시키는 역할을 합니다. 이 순환은 엔진이 최적의 작동 온도를 유지할 수 있도록 하여 과열을 방지하고 효율적인 성능을 보장합니다.
- 기본 기능: 워터 펌프는 회전하는 임펠러가 생성하는 원심력을 이용하여 냉각수를 엔진 블록, 실린더 헤드, 그리고 궁극적으로 라디에이터로 밀어냅니다. 냉각수는 엔진에서 열을 흡수하고 라디에이터를 통해 공기 흐름에 의해 냉각됩니다.
- 냉각 시스템 통합: 워터 펌프는 라디에이터, 서모스탯, 호스 및 다양한 센서가 포함된 차량의 냉각 시스템에 통합되어 있습니다. 이 시스템은 함께 작동하여 엔진 온도를 조절하고, 엔진의 효율성과 수명을 향상합니다.
1.2. 워터 펌프의 구성 요소
일반적인 자동차 워터 펌프는 다음과 같은 주요 구성 요소로 이루어져 있어 효과적으로 기능을 수행합니다:
- 하우징: 워터 펌프의 외부 케이싱으로, 일반적으로 알루미늄이나 주철로 만들어집니다. 내부 구성 요소를 보호하며, 높은 압력과 온도를 견딜 수 있도록 설계되었습니다.
- 임펠러: 엔진이 작동할 때 회전하는 팬 모양의 구성 요소입니다. 임펠러의 날개는 원심력을 생성하여 냉각수를 펌프 안으로 끌어들이고, 냉각수를 냉각 시스템으로 밀어냅니다.
- 샤프트: 임펠러를 엔진의 크랭크샤프트에 연결하는 금속 막대입니다. 샤프트는 엔진과 함께 회전하며 임펠러를 구동합니다.
- 씰과 베어링: 씰은 냉각수가 펌프 밖으로 새지 않도록 방지하고, 베어링은 샤프트를 지탱하며 부드러운 회전을 가능하게 합니다.
- 개스킷: 워터 펌프와 엔진 블록 사이에 위치하여 누수를 방지하는 밀폐재입니다.
1.3. 역사와 발전
워터 펌프의 개념은 자동차 공학 초기 시절로 거슬러 올라갑니다. 초기 설계는 비교적 단순하고 기계적이었으며, 엔진에 의해 직접 구동되었습니다.
- 초기 설계: 초기 워터 펌프는 일반적으로 기어 구동 방식이었으며, 수동 조정이 필요했습니다. 자동차 기술이 발전함에 따라 워터 펌프의 설계와 효율성도 발전했습니다.
- 현대적 발전: 오늘날의 워터 펌프는 벨트 구동식 또는 전기식으로, 더욱 향상된 효율성과 엔진에 대한 부담 감소를 제공합니다. 내구성과 성능을 향상하기 위해 고급 재료와 디자인이 도입되었습니다.
2. 기능과 중요성
2.1. 엔진 냉각에서의 역할
워터 펌프는 냉각수를 적절히 순환시켜 엔진 온도를 유지하는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다. 다음은 엔진 냉각에 기여하는 방식입니다:
- 열 흡수: 엔진이 작동하면 연소로 인해 열이 발생합니다. 워터 펌프는 냉각수를 순환시켜 이 열을 흡수하고 엔진 과열을 방지합니다.
- 온도 조절: 워터 펌프는 엔진 온도에 따라 냉각수 흐름을 조절하는 서모스탯과 함께 작동합니다. 엔진이 차가울 때 서모스탯은 닫혀 있어 빠른 예열을 가능하게 하고, 엔진이 최적 온도에 도달하면 열려 냉각수가 라디에이터로 흐르도록 합니다.
2.2. 엔진 성능에 미치는 영향
워터 펌프의 효율성은 엔진 성능과 수명에 직접적인 영향을 미칩니다. 효과적인 냉각 시스템은 엔진이 설계된 온도 범위 내에서 작동하도록 보장하여 여러 가지 이점을 제공합니다:
- 효율성 향상: 최적의 온도에서 작동하는 엔진은 보다 효율적으로 성능을 발휘하여 연료 경제성과 배출가스를 개선합니다.
- 손상 예방: 과열은 엔진 부품에 심각한 손상을 초래할 수 있습니다. 워터 펌프가 정상 작동하면 냉각수를 지속적으로 순환시켜 과열을 방지합니다.
- 수명 연장: 정기적으로 작동하는 워터 펌프는 엔진의 전반적인 수명을 늘리는데 기여합니다. 일관된 냉각은 엔진 부품의 마모를 최소화하고 조기 고장의 가능성을 줄입니다.
2.3. 워터 펌프 고장의 징후
워터 펌프의 고장을 조기에 인식하는 것은 엔진 손상을 방지하는 데 중요합니다. 일반적인 징후는 다음과 같습니다:
- 엔진 과열: 엔진 온도 게이지가 정상 수준을 초과하면 워터 펌프가 냉각수를 효과적으로 순환시키지 못하고 있을 수 있습니다.
- 냉각수 누수: 차량 아래나 워터 펌프 주변에서 냉각수가 고인 물이 보이면 씰이나 개스킷의 누수로 인해 발생할 수 있습니다.
- 이상 소음: 고장 난 워터 펌프는 마모된 베어링이나 임펠러 문제로 인해 갈리거나 끼익 거리는 소리를 낼 수 있습니다.
- 엔진 구역에서의 증기: 엔진 후드 아래에서 과도한 증기나 냉각수 증기가 발생하면 과열을 나타내며, 이는 종종 워터 펌프의 고장으로 인해 발생합니다.
3. 유형, 유지 관리 및 교체
3.1. 워터 펌프의 유형
자동차에 사용되는 다양한 유형의 워터 펌프가 있으며, 각각 특정 용도에 맞게 설계되어 있습니다. 가장 일반적인 유형은 다음과 같습니다:
- 원심 워터 펌프: 가장 널리 사용되는 유형으로, 원심 펌프는 임펠러를 사용하여 냉각수를 이동시킵니다. 대부분의 자동차 응용에서 효율적이고 효과적입니다.
- 전기 워터 펌프: 이 펌프는 엔진과 독립적으로 작동하며, 주로 하이브리드 또는 전기 차량에서 사용됩니다. 냉각수 흐름과 온도 관리를 더 잘 제어할 수 있습니다.
- 기계식 워터 펌프: 엔진의 크랭크샤프트에 연결된 벨트에 의해 구동되는 기계식 펌프는 많은 내연기관 차량에서 표준으로 사용됩니다.
- 가변 유량 펌프: 일부 최신 차량은 엔진 수요에 따라 유량을 조절하는 가변 유량 워터 펌프를 사용하여 효율성을 높입니다.
3.2. 유지 관리 팁
워터 펌프와 냉각 시스템의 적절한 유지 관리는 최적의 성능과 수명을 보장하는 데 필수적입니다. 다음은 몇 가지 유지 관리 팁입니다:
- 정기적인 냉각수 점검: 냉각수의 수위와 상태를 정기적으로 점검합니다. 냉각수가 깨끗하고 오염물이 없는지 확인하고, 제조업체의 권장에 따라 교체합니다.
- 누수 점검: 정기적으로 워터 펌프와 주변 지역을 점검하여 냉각수 누수의 징후가 있는지 확인합니다. 누수가 발견되면 즉시 해결하여 과열을 방지합니다.
- 소음에 주의: 워터 펌프에서 나오는 비정상적인 소음에 주의합니다. 갈리거나 끼익 거리는 소리가 들리면 문제의 징후일 수 있으므로 점검이 필요합니다.
- 필요시 교체: 워터 펌프는 일반적으로 60,000~100,000마일의 수명을 가집니다. 고장의 징후가 있거나 펌프가 수명에 가까운 경우, 엔진 손상을 방지하기 위해 교체하는 것이 좋습니다.
3.3. 교체 과정
워터 펌프를 교체해야 할 경우, 올바른 설치를 보장하기 위해 체계적인 접근이 필요합니다. 다음은 워터 펌프 교체에 일반적으로 포함되는 단계입니다:
1. 준비: 필요한 도구와 교체용 워터 펌프를 준비합니다. 차량이 평평한 표면에 위치하도록 하고 배터리를 분리합니다.
2. 냉각수 배출: 라디에이터와 엔진에서 냉각수를 배출하여 교체 과정 중 누수를 방지합니다.
3. 구성 요소 제거: 차량에 따라 라디에이터 호스, 벨트, 엔진 커버 등 다양한 구성 요소를 제거해야 워터 펌프에 접근할 수 있습니다.
4. 기존 워터 펌프 제거: 기존 워터 펌프를 하우징에서 분리하고 조심스럽게 제거합니다. 오래된 개스킷 재료를 제거하여 장착 면을 청소합니다.
5. 새로운 워터 펌프 설치: 새로운 워터 펌프를 제자리에 놓고 장착 구멍과 올바르게 정렬되도록 합니다. 새로운 개스킷을 설치하고 볼트를 제조업체의 사양에 맞게 조입니다.
6. 구성 요소 재조립: 제거한 구성 요소를 재조립합니다. 필요시 라디에이터 호스를 다시 연결하고, 벨트를 다시 장착합니다.
7. 냉각수 보충: 적절한 냉각수 혼합물로 냉각 시스템을 다시 채웁니다. 엔진을 시작하고 누수 여부를 확인하며 냉각수 순환이 제대로 이루어지는지 점검합니다.
8. 테스트 드라이브: 차량을 테스트 드라이브하여 새로운 워터 펌프가 정상적으로 작동하는지, 엔진이 적절한 온도를 유지하는지 확인합니다.
결론
워터 펌프는 자동차의 냉각 시스템에서 필수적인 구성 요소로, 최적의 엔진 온도와 성능을 유지하는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다. 그 기능, 유형 및 유지 관리 요건을 이해하는 것은 차량 소유자에게 필수적입니다. 정기적인 점검과 시기적절한 교체는 심각한 엔진 손상을 방지하고 차량의 전반적인 효율성을 향상합니다. 워터 펌프 고장의 징후를 인식하고 일상적인 유지 관리를 수행함으로써 운전자는 엔진을 보호하고 차량 성능을 개선할 수 있습니다.
1. Overview of Water Pumps
1.1. Definition and Purpose
A water pump is a critical component in an automobile's cooling system, designed to circulate coolant (a mixture of water and antifreeze) through the engine and radiator. This circulation helps maintain the engine at an optimal operating temperature, preventing overheating and ensuring efficient performance.
- Basic Functionality: The water pump operates by using a centrifugal force generated by a rotating impeller to push coolant through the engine block, cylinder head, and ultimately to the radiator. The coolant absorbs heat from the engine and releases it through the radiator, where it is cooled by airflow.
- Cooling System Integration: The water pump is integrated into the vehicle’s cooling system, which includes the radiator, thermostat, hoses, and various sensors. This system works together to regulate engine temperature, thereby enhancing engine efficiency and longevity.
1.2. Components of a Water Pump
A typical automotive water pump consists of several key components that work together to perform its function effectively:
- Housing: The outer casing of the water pump, usually made of aluminum or cast iron, houses the internal components. It is designed to withstand high pressure and temperature.
- Impeller: A fan-like component that rotates when the engine is running. The impeller's blades create a centrifugal force that draws coolant into the pump and pushes it out into the cooling system.
- Shaft: A metal rod that connects the impeller to the engine's crankshaft. The shaft rotates with the engine, driving the impeller.
- Seals and Bearings: Seals prevent coolant from leaking out of the pump, while bearings support the shaft and allow for smooth rotation.
- Gasket: A sealing material placed between the water pump and the engine block to prevent leaks.
1.3. History and Evolution
The concept of the water pump dates back to the early days of automotive engineering. Initial designs were relatively simple and mechanical, driven directly by the engine.
- Early Designs: Early water pumps were typically gear-driven and required manual adjustments. As automotive technology evolved, so did the design and efficiency of water pumps.
- Modern Developments: Today’s water pumps are often belt-driven or electrically powered, allowing for improved efficiency and reduced strain on the engine. Advanced materials and designs have also been introduced to enhance durability and performance.
2. Function and Importance in Vehicle Cooling Systems
2.1. Role in Engine Cooling
The water pump plays a vital role in maintaining the engine's temperature by ensuring the proper flow of coolant. Here’s how it contributes to engine cooling:
- Heat Absorption: As the engine operates, it generates heat due to combustion. The water pump circulates coolant, which absorbs this heat and prevents the engine from overheating.
- Temperature Regulation: The water pump works in conjunction with the thermostat, a temperature-sensitive valve that regulates coolant flow based on the engine's temperature. When the engine is cold, the thermostat remains closed to allow for faster warming. As the engine reaches optimal temperature, the thermostat opens, allowing coolant to flow through the radiator.
2.2. Impact on Engine Performance
The efficiency of the water pump directly affects engine performance and longevity. An effective cooling system ensures that the engine operates within its designed temperature range, which has several benefits:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Engines running at optimal temperatures perform more efficiently, leading to better fuel economy and reduced emissions.
- Prevention of Damage: Overheating can cause severe damage to engine components, leading to costly repairs. A functioning water pump helps prevent overheating by maintaining coolant circulation.
- Longevity: Regularly functioning water pumps contribute to the overall longevity of the engine. Consistent cooling minimizes wear and tear on engine parts, reducing the likelihood of premature failure.
2.3. Signs of Water Pump Failure
Recognizing the signs of a failing water pump is crucial for preventing engine damage. Common indicators include:
- Overheating Engine: If the engine temperature gauge rises above normal levels, it may indicate that the water pump is not circulating coolant effectively.
- Coolant Leaks: Puddles of coolant under the vehicle or around the water pump area can indicate a leak due to a failing seal or gasket.
- Unusual Noises: A failing water pump may produce grinding or whining noises due to worn bearings or impeller issues.
- Steam from Engine Compartment: Excessive steam or coolant vapor coming from under the hood can signal overheating, often due to a malfunctioning water pump.
3. Types, Maintenance, and Replacement
3.1. Types of Water Pumps
Various types of water pumps are used in automobiles, each designed for specific applications. The most common types include:
- Centrifugal Water Pumps: The most widely used type, centrifugal pumps rely on an impeller to move coolant. They are efficient and effective for most automotive applications.
- Electric Water Pumps: These pumps operate independently of the engine and are often used in hybrid or electric vehicles. They can provide better control over coolant flow and temperature management.
- Mechanical Water Pumps: Driven by a belt connected to the engine’s crankshaft, mechanical pumps are standard in many internal combustion engine vehicles.
- Variable Flow Pumps: Some modern vehicles utilize variable flow water pumps, which adjust the flow rate based on engine demands, enhancing efficiency.
3.2. Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance of the water pump and cooling system is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here are some maintenance tips:
- Regular Coolant Checks: Regularly check the coolant level and condition. Ensure the coolant is clean and free from contaminants, and replace it as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Inspect for Leaks: Periodically inspect the water pump and surrounding areas for signs of coolant leaks. Address any leaks promptly to prevent overheating.
- Listen for Noises: Pay attention to any unusual noises coming from the water pump. If you hear grinding or whining sounds, it may indicate a problem that needs attention.
- Replace as Needed: Water pumps typically have a lifespan of around 60,000 to 100,000 miles. If you experience any signs of failure or if the pump is nearing the end of its lifespan, consider replacing it to avoid catastrophic engine damage.
3.3. Replacement Process
When the water pump needs to be replaced, it is essential to follow a systematic approach to ensure proper installation. Here are the general steps involved in replacing a water pump:
1. Preparation: Gather the necessary tools and a replacement water pump. Ensure the vehicle is on a level surface, and disconnect the battery.
2. Drain Coolant: Drain the engine coolant from the radiator and engine to prevent spills during the replacement process.
3. Remove Components: Depending on the vehicle, you may need to remove various components, such as the radiator hose, serpentine belt, and any engine covers, to access the water pump.
4. Remove Old Water Pump: Unbolt the old water pump from its housing and carefully remove it. Clean the mounting surface to remove any old gasket material.
5. Install New Water Pump: Position the new water pump in place, ensuring it aligns correctly with the mounting holes. Install the new gasket and tighten the bolts to the manufacturer’s specifications.
6. Reassemble Components: Reinstall any components that were removed during the process. Reconnect the radiator hose and serpentine belt if applicable.
7. Refill Coolant: Refill the cooling system with the appropriate coolant mixture. Start the engine and let it run while checking for leaks and ensuring proper coolant circulation.
8. Test Drive: Take the vehicle for a test drive to ensure the new water pump is functioning correctly and that the engine is maintaining the proper temperature.
Conclusion
The water pump is an essential component of an automobile's cooling system, playing a crucial role in maintaining optimal engine temperature and performance. Understanding its function, types, and maintenance requirements is vital for vehicle owners to ensure longevity and reliability. Regular inspection and timely replacement of the water pump can prevent significant engine damage and improve the overall efficiency of the vehicle. By recognizing the signs of water pump failure and performing routine maintenance, drivers can safeguard their engines and enhance their vehicles' performance.